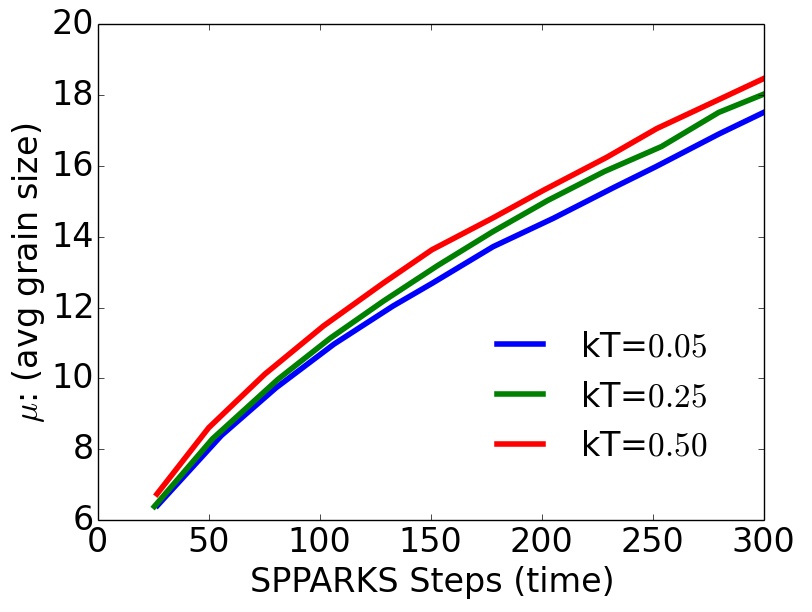
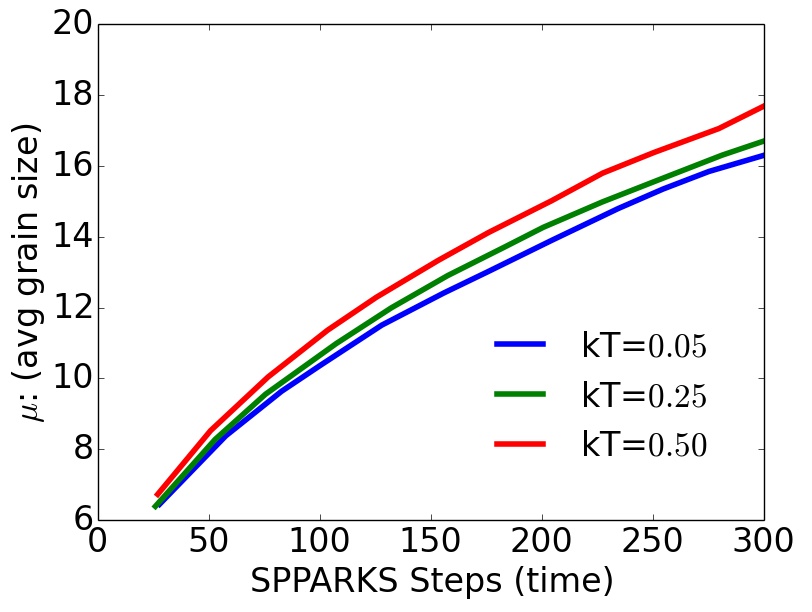
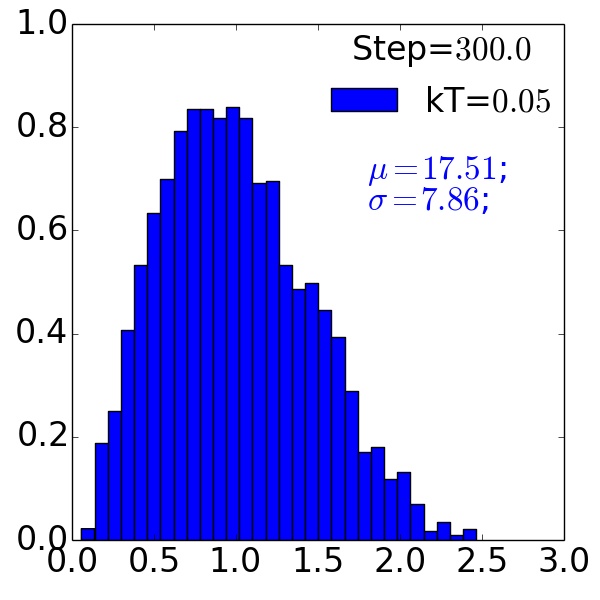
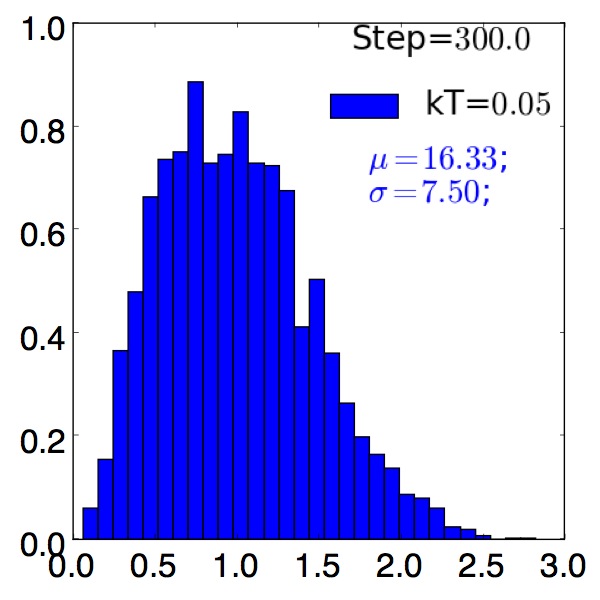
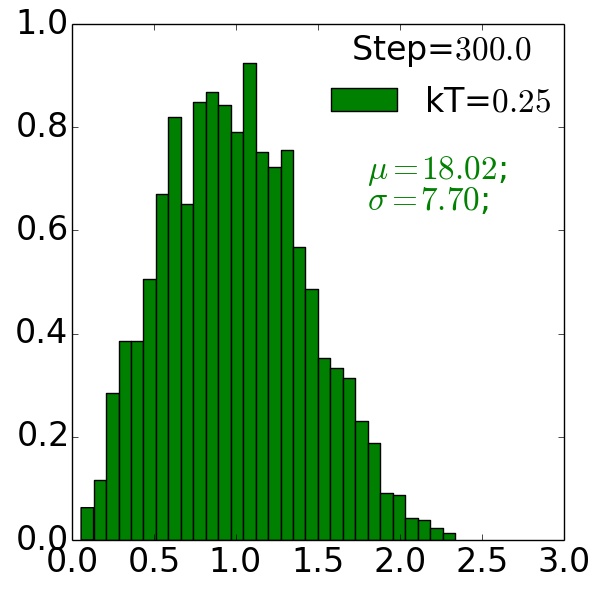
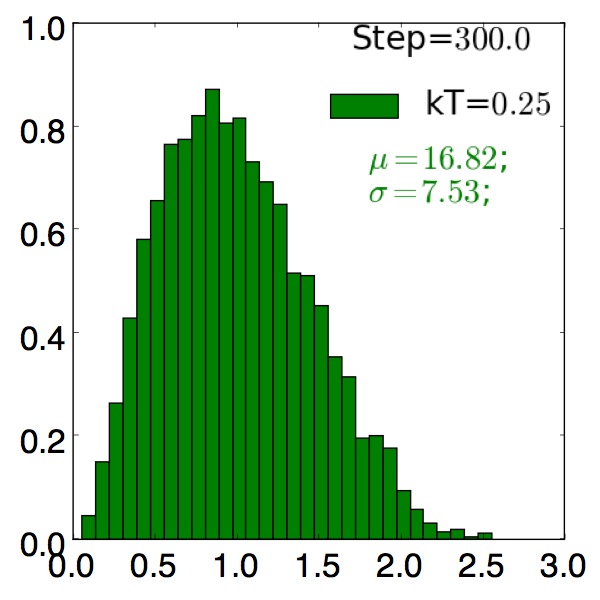
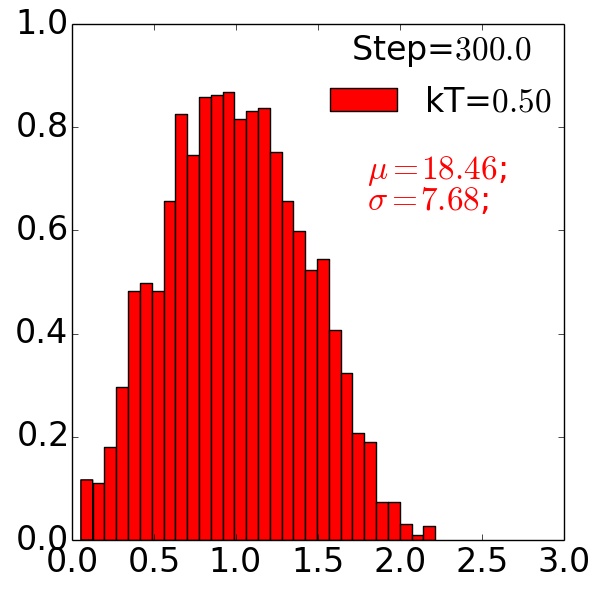
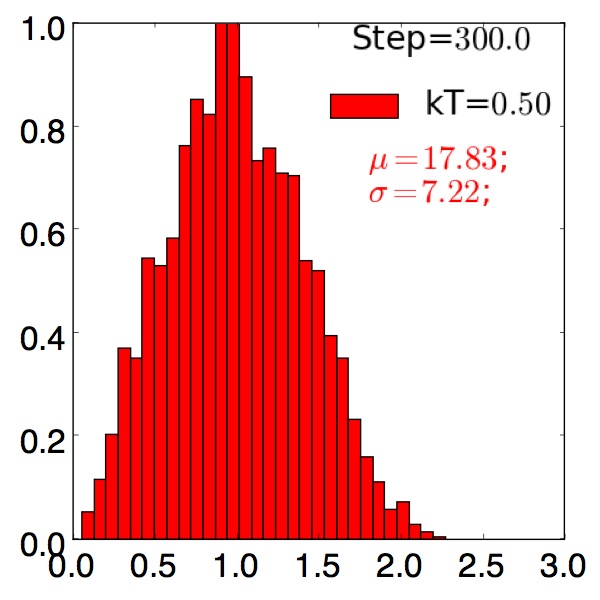
Grain Size Distributions¶
Compare grain growth with and without precipitate
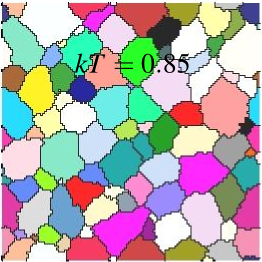
Lattice: 128x128; (spparks rendered): dump image:
without precipitate
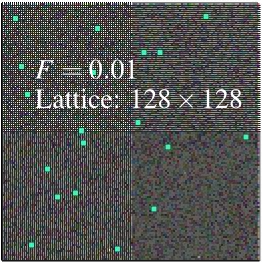
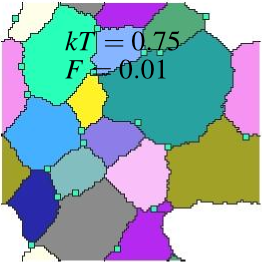
Lattice: 128x128; (spparks rendered): dump image:
with precipitate, F=0.01
Post-process and analyze grain-size distributions
Summary of key points¶
- Model normal isotropic grain growth using the potts model
- Include single precipitate using spparks pin command
- Visualize and analyze similarly to case without precipitate
- Observe precipitate slows grain growth
- Also see Rules of Thumb for Potts Model