Summary of key points¶

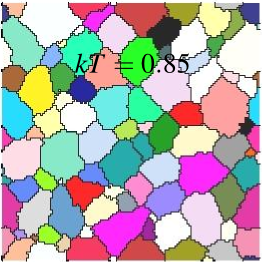
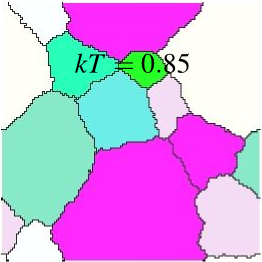
Modeling and Analysis¶
- Model normal isotropic grain growth using the potts model
- spparks can run serial or parallel, 2- or 3D
- Visualize grains using paraview or render images directly from spparks
- Post process dump files for analysis
Rules of Thumb for Potts Model¶
- Use large number of spin values \(Q\) (thousands)
- Use temperatures \(T_f\leq kT\leq T_r\)
\(T_r, T_f\) depend on lattice and dimensionality
- \(T_f\), mesh pinning temperature
- \(T_r\), grain boundary roughening temperature
Trends as \(kT\) increases:
- Rate of grain growth increases
- Standard deviation \(\sigma\) may decrease
For \(kT\gt T_r\)
- Model exhibits grain boundary roughening
- Excessive single site grains
For \(kT\lt T_f\)
- Grain exhibit mesh pinning
- Grains lock onto underlying lattice;
Visualize grains
Plot distributions